Candida albicans-Epithelial Interactions: Dissecting the Roles of Active Penetration, Induced Endocytosis and Host Factors on the Infection Process | PLOS ONE
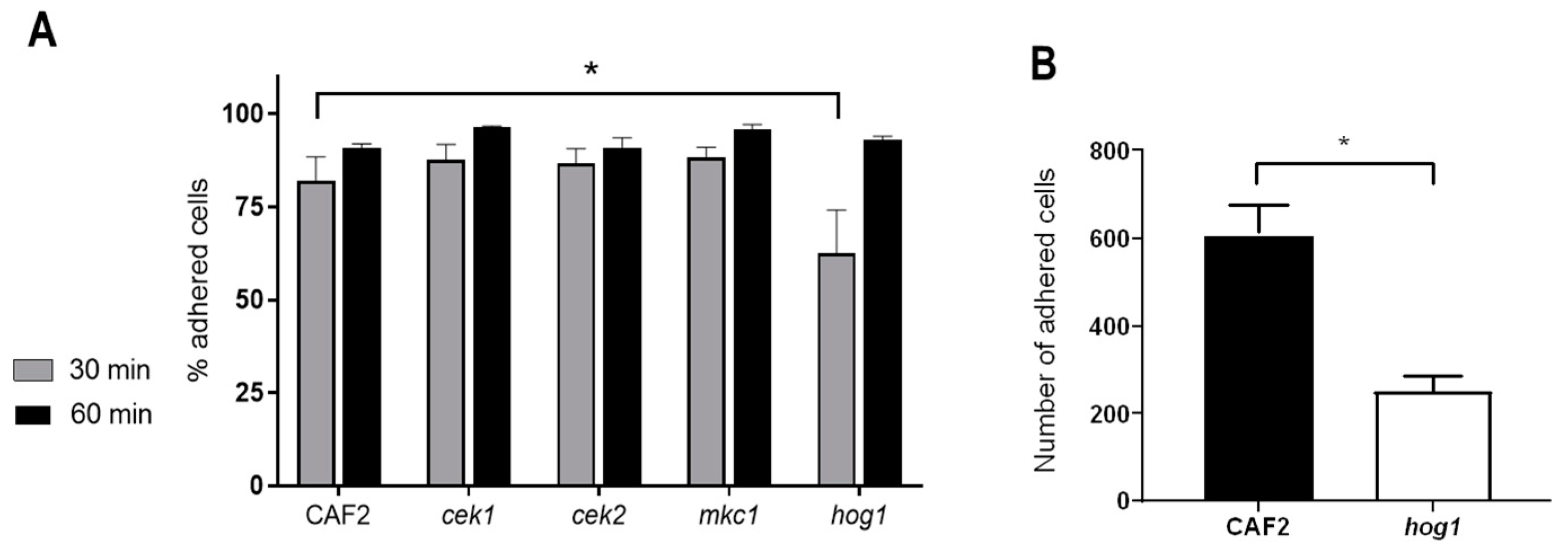
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Cooperative Role of MAPK Pathways in the Interaction of Candida albicans with the Host Epithelium
From Attachment to Damage: Defined Genes of Candida albicans Mediate Adhesion, Invasion and Damage during Interaction with Oral Epithelial Cells | PLOS ONE

Cytokine activation and cell damage by different Candida species and S.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Oral epithelial cells orchestrate innate type 17 responses to Candida albicans through the virulence factor candidalysin | Science Immunology

Activation of MKP1 and c-Fos signaling by C. albicans Dals mutants. C.... | Download Scientific Diagram

ERG3 and ERG11 genes are critical for the pathogenesis of Candida albicans during the oral mucosal infection | International Journal of Oral Science
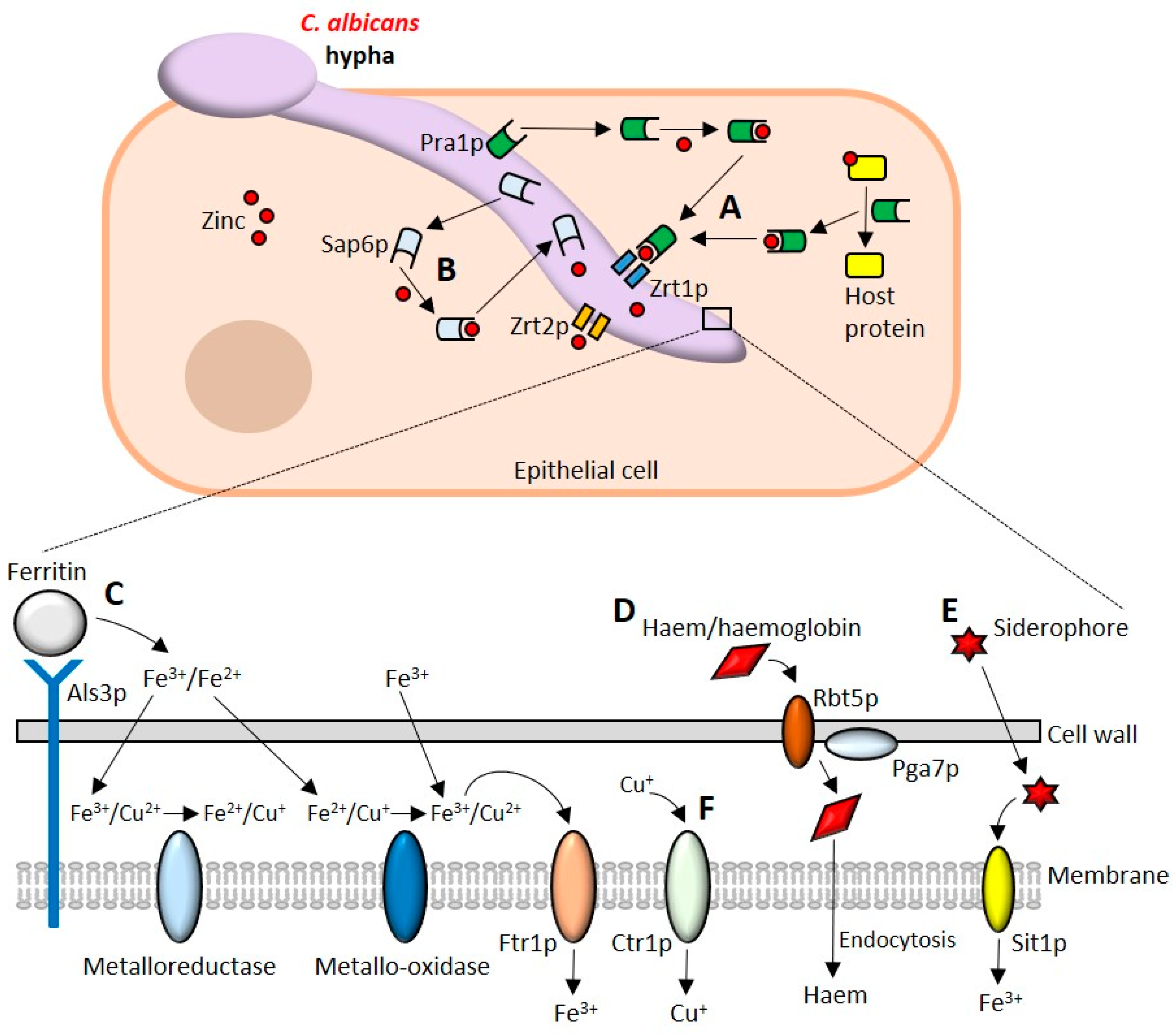
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans Interactions with Mucosal Surfaces during Health and Disease
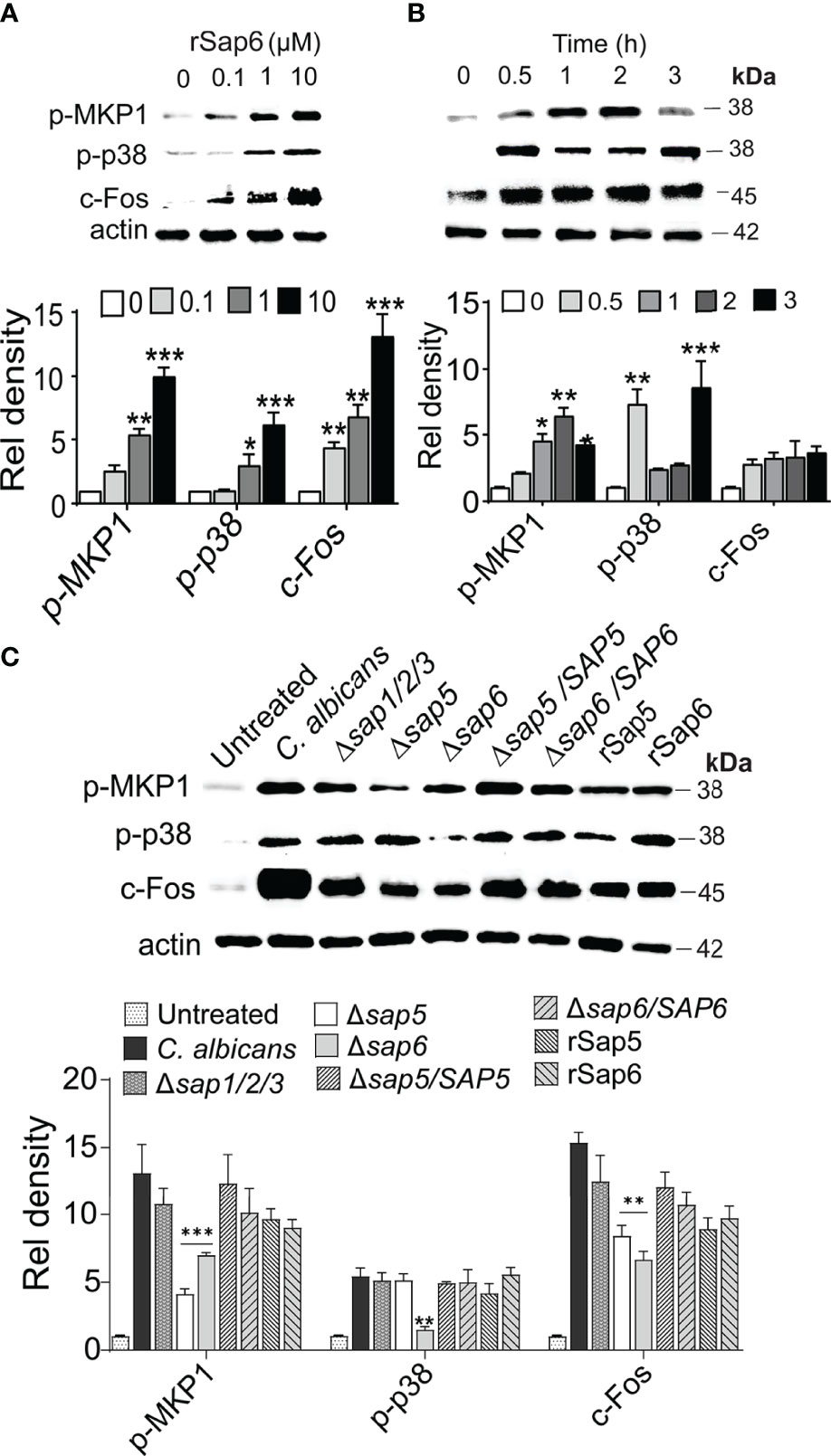
Frontiers | Candida albicans Sap6 Initiates Oral Mucosal Inflammation via the Protease Activated Receptor PAR2
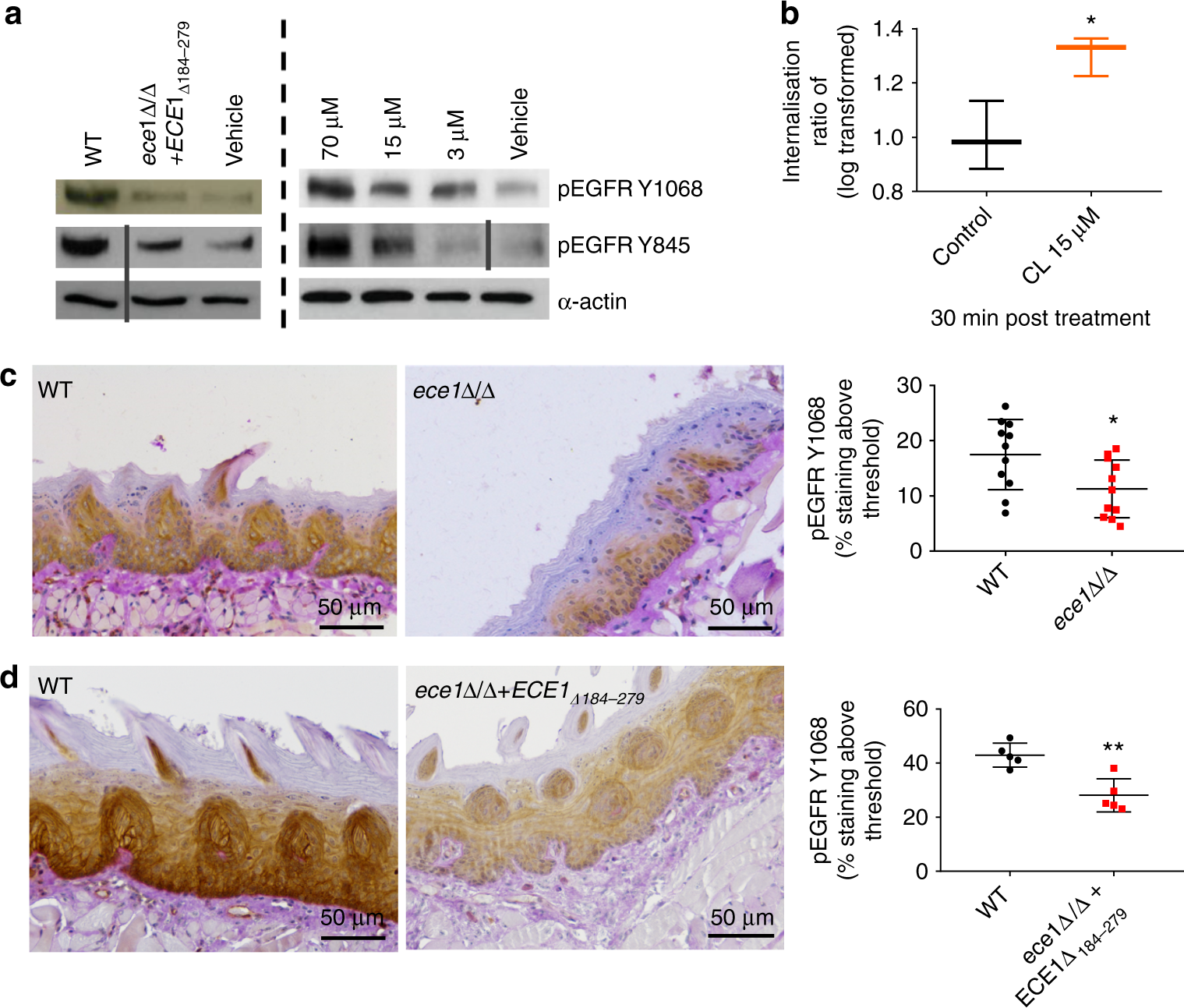
Candidalysin activates innate epithelial immune responses via epidermal growth factor receptor | Nature Communications
Candida albicans commensalism in the oral mucosa is favoured by limited virulence and metabolic adaptation | PLOS Pathogens

Model for protective innate immune responses against C albicans at oral... | Download Scientific Diagram

Activation of MAPK/c-Fos induced responses in oral epithelial cells is specific to Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis hyphae | SpringerLink
Processing of <italic toggle='yes'>Candida albicans</italic> Ece1p Is Critical for Candidalysin Maturation a

The Candida albicans toxin candidalysin mediates distinct epithelial inflammatory responses through p38 and EGFR-ERK pathways | Science Signaling

PDF) Candida albicans Cell Wall Glycosylation May Be Indirectly Required for Activation of Epithelial Cell Proinflammatory Responses

Oral epithelial cells orchestrate innate type 17 responses to Candida albicans through the virulence factor candidalysin | Science Immunology
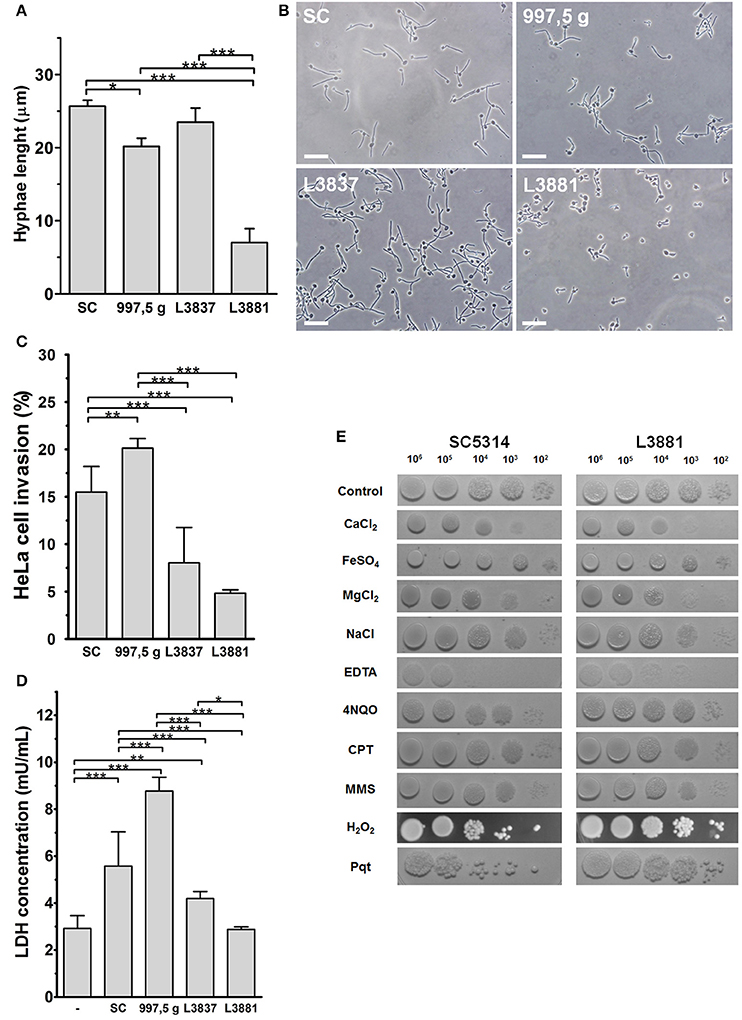
Frontiers | Candida albicans: The Ability to Invade Epithelial Cells and Survive under Oxidative Stress Is Unlinked to Hyphal Length

Cellular interactions of Candida albicans with human oral epithelial cells and enterocytes - Dalle - 2010 - Cellular Microbiology - Wiley Online Library

The Candida albicans toxin candidalysin mediates distinct epithelial inflammatory responses through p38 and EGFR-ERK pathways | Science Signaling

Candida albicans Cell Wall Glycosylation May Be Indirectly Required for Activation of Epithelial Cell Proinflammatory Responses | Infection and Immunity






