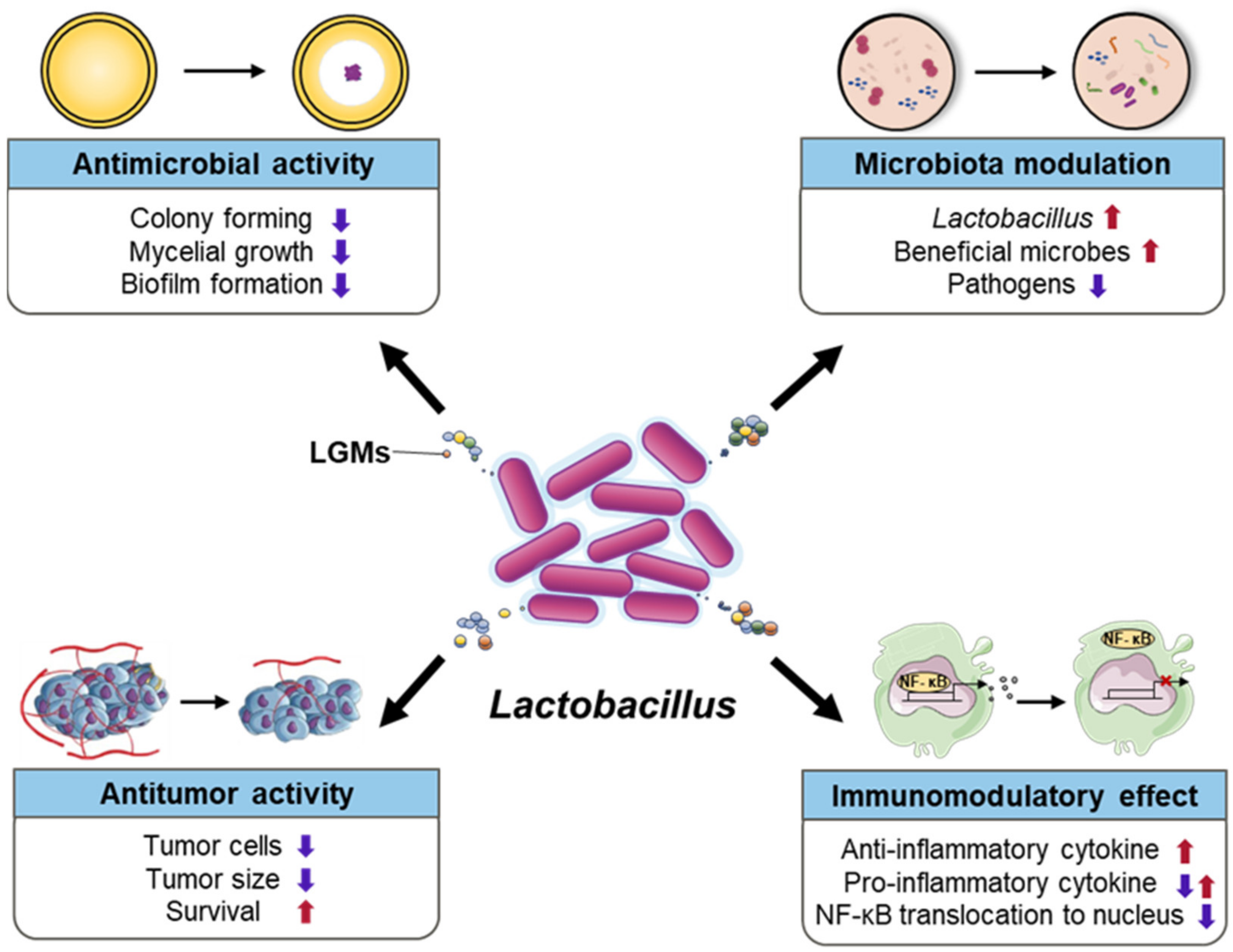
Inflammatory and antimicrobial properties differ between vaginal Lactobacillus isolates from South African women with non-optimal versus optimal microbiota | Scientific Reports

Surface-Layer Protein from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation through MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in RAW264.7 Cells | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry

Stimulation of Probiotic Bacteria Induces Release of Membrane Vesicles with Augmented Anti-inflammatory Activity | ACS Applied Bio Materials
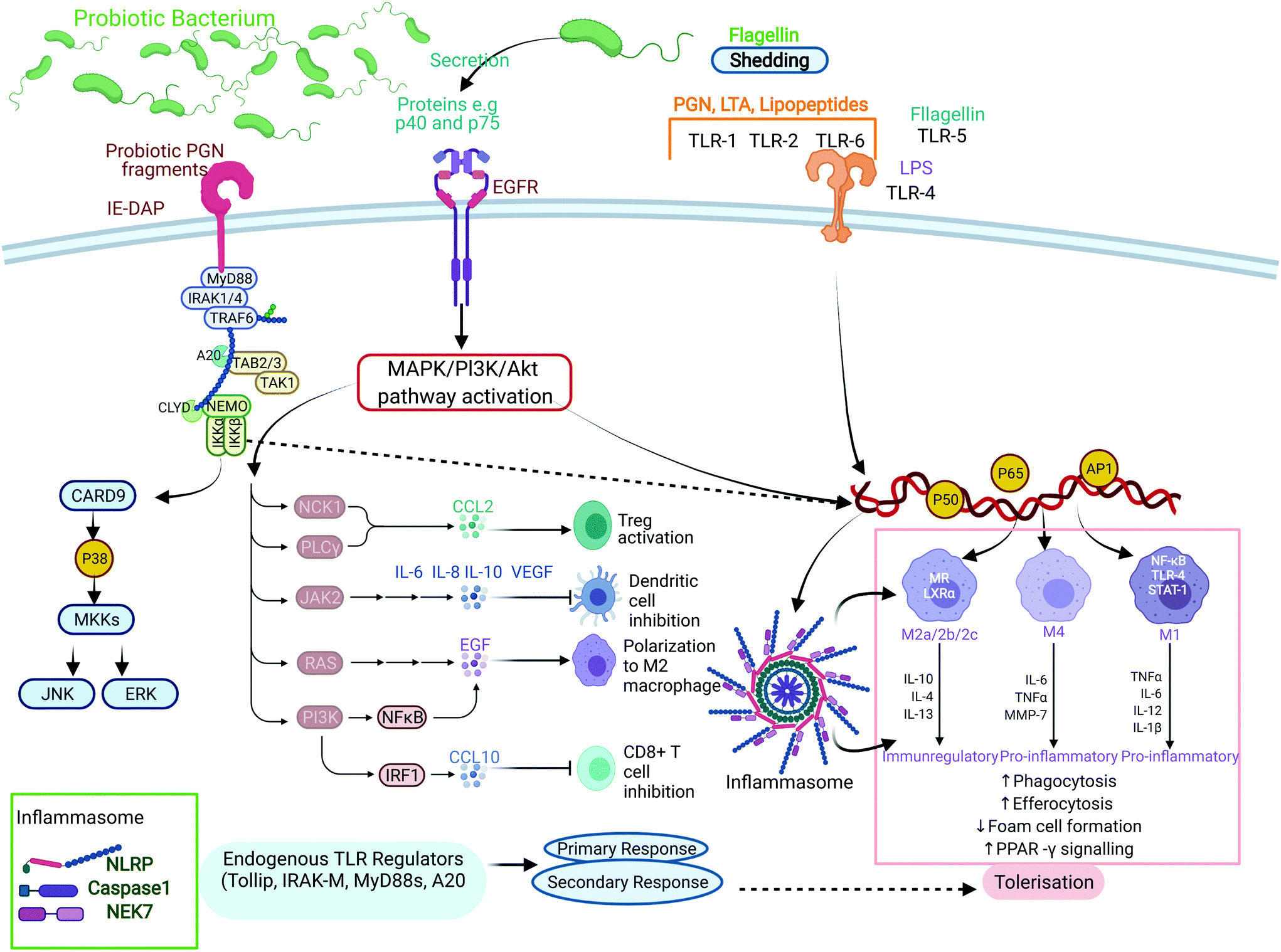
Probiotics and gut microbiota: mechanistic insights into gut immune homeostasis through TLR pathway regulation - Food & Function (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2FO00911K
View of <em>Lactobacillus plantarum</em> Lp2 improved LPS-induced liver injury through the TLR-4/MAPK/NFκB and Nrf2-HO-1/CYP2E1 pathways in mice | Food & Nutrition Research

Lactobacillus paracasei modulates LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine release by monocyte-macrophages via the up-regulation of negative regulators of NF-kappaB signaling in a TLR2-dependent manner - ScienceDirect
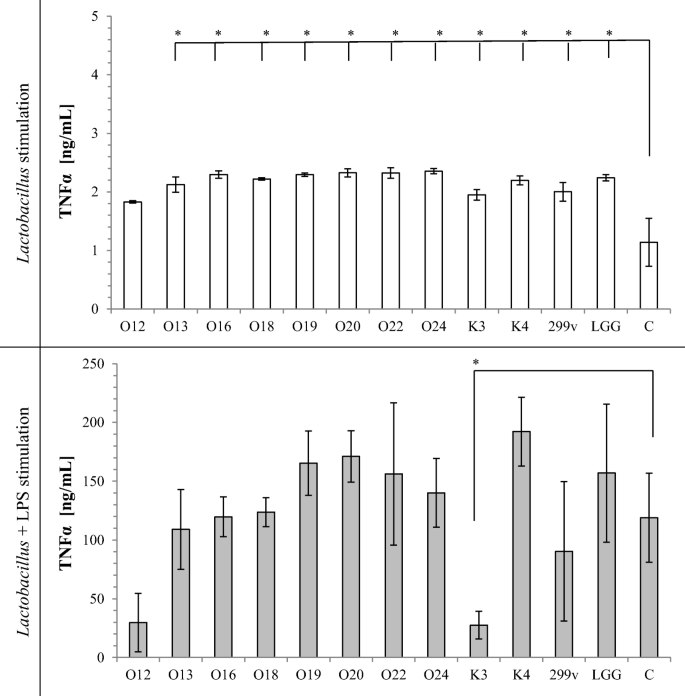
Functional Properties of Food Origin Lactobacillus in the Gastrointestinal Ecosystem—In Vitro Study | SpringerLink

Surface-Layer Protein from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation through MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in RAW264.7 Cells | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
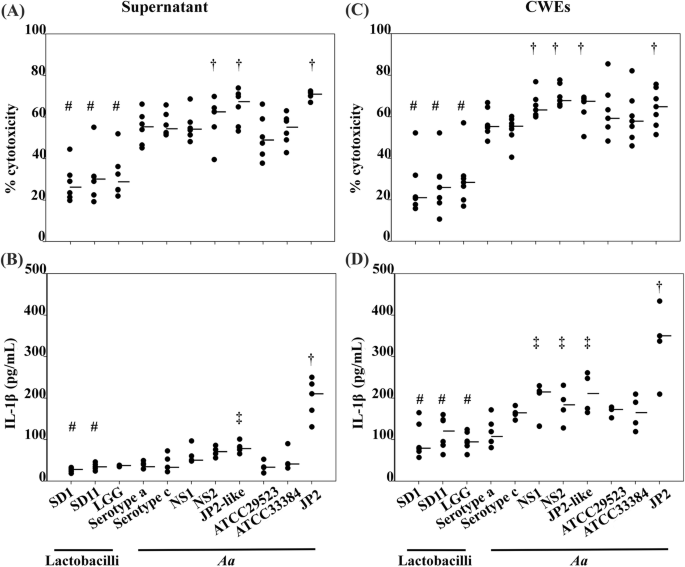
Oral Lactobacillus strains reduce cytotoxicity and cytokine release from peripheral blood mononuclear cells exposed to Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans subtypes in vitro | BMC Microbiology | Full Text

Milk fermented with Lactobacillus rhamnosus R0011 induces a regulatory cytokine profile in LPS-challenged U937 and THP-1 macrophages | Semantic Scholar
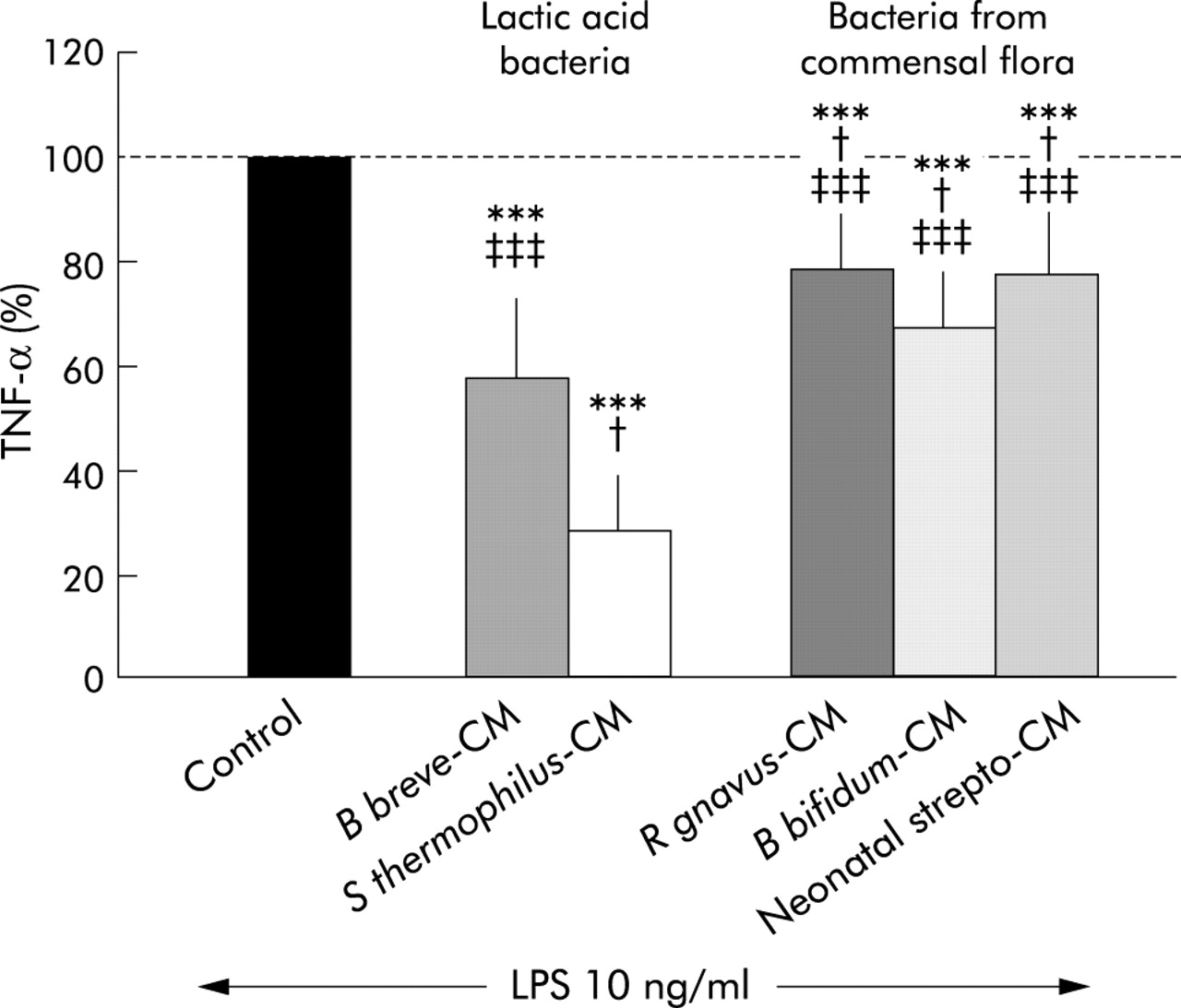
Lactic acid bacteria secrete metabolites retaining anti-inflammatory properties after intestinal transport | Gut

Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 is a unique prophylactic agent that suppresses infection-induced myometrial cell responses | Scientific Reports

Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Profiles of Cytokine, Chemokine, and Growth Factors Produced by Human Decidual Cells Are Altered by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 Supernatant - Wei Li, Siwen Yang, Sung O. Kim, Gregor Reid, John R. G.

Frontiers | Lactobacillus plantarum RS-09 Induces M1-Type Macrophage Immunity Against Salmonella Typhimurium Challenge via the TLR2/NF-κB Signalling Pathway

Lactobacillus rhamnosus protects human colonic muscle from pathogen lipopolysaccharide‐induced damage - Ammoscato - 2013 - Neurogastroenterology & Motility - Wiley Online Library
Soluble Factors from Lactobacillus reuteri CRL1098 Have Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Acute Lung Injury Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in Mice | PLOS ONE

Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG decreases TNF‐α production in lipopolysaccharide‐activated murine macrophages by a contact‐independent mechanism - Peña - 2003 - Cellular Microbiology - Wiley Online Library

Milk fermented with Lactobacillus rhamnosus R0011 induces a regulatory cytokine profile in LPS-challenged U937 and THP-1 macrophages | Semantic Scholar

Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum strains on the expression levels of... | Download Scientific Diagram

Selected lactobacilli strains inhibit inflammation in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing the TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPKs activation
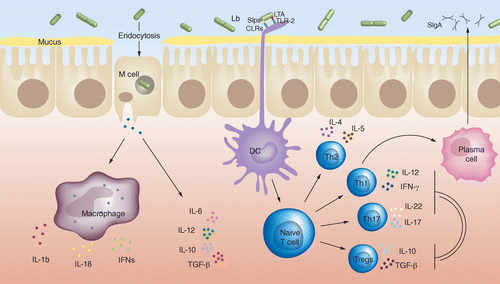
Immunomodulatory effects of Lactobacillus strains: emphasis on their effects on cancer cells | Immunotherapy

OBM Hepatology and Gastroenterology | Multi-Species Probiotic Modulates Cytokine Production and the Interplay between Immune and Colon Cancer Cells