Adapting to survive: How Candida overcomes host-imposed constraints during human colonization | PLOS Pathogens

Serum Amyloid P Component Binds Fungal Surface Amyloid and Decreases Human Macrophage Phagocytosis and Secretion of Inflammatory Cytokines | mBio

Metabolism impacts upon Candida immunogenicity and pathogenicity at multiple levels: Trends in Microbiology
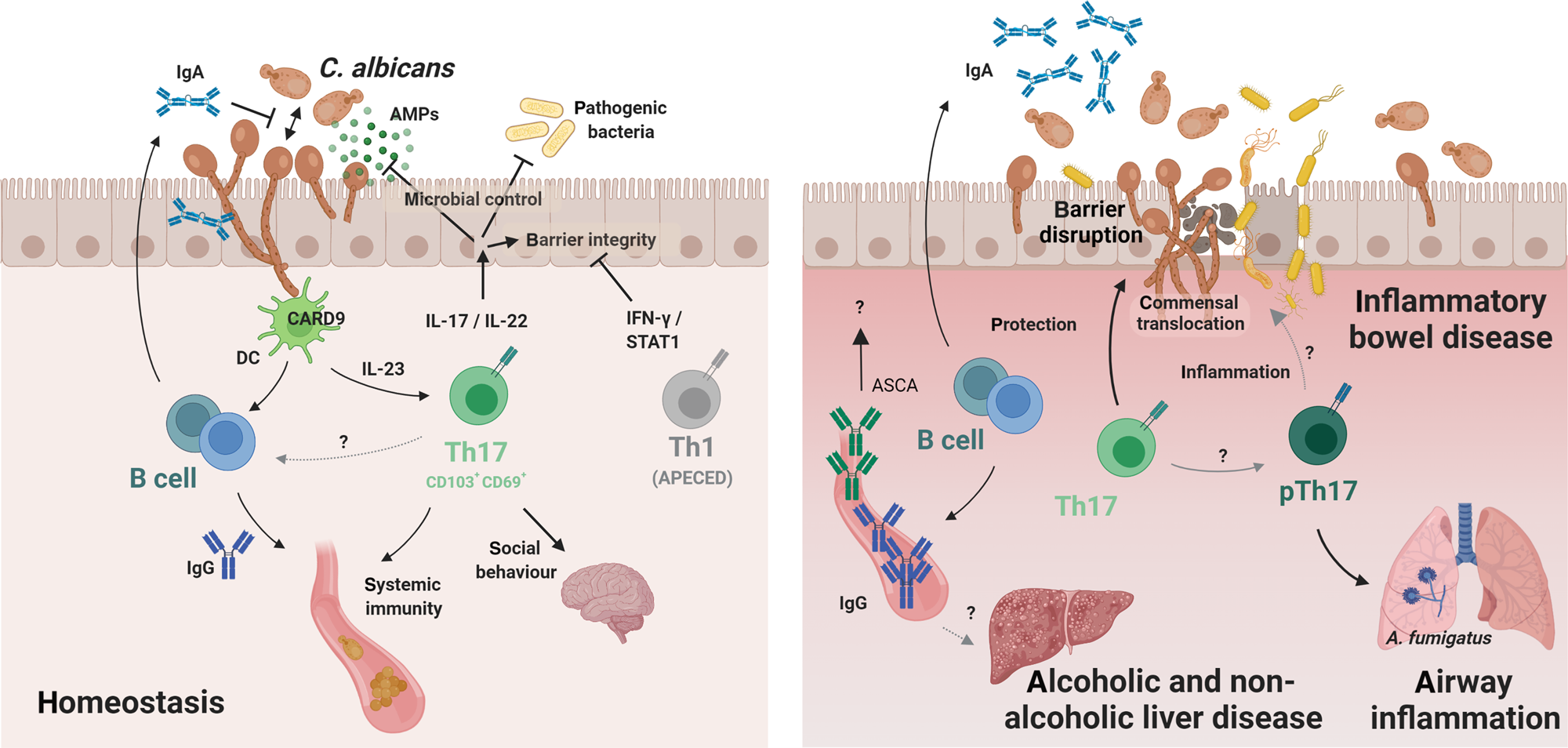
Immunosurveillance of Candida albicans commensalism by the adaptive immune system | Mucosal Immunology
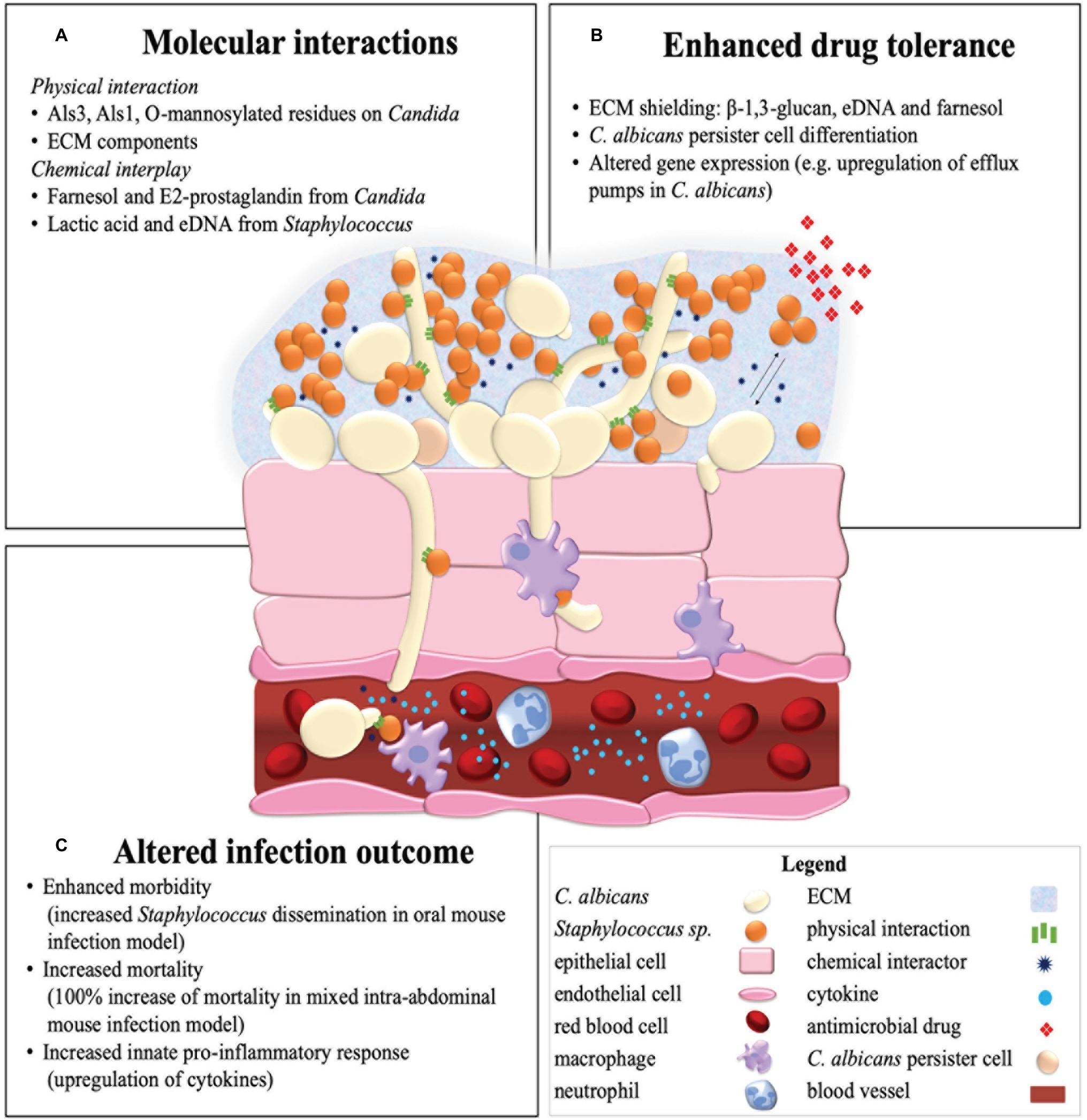
Full article: Candida albicans-epithelial interactions and pathogenicity mechanisms: scratching the surface
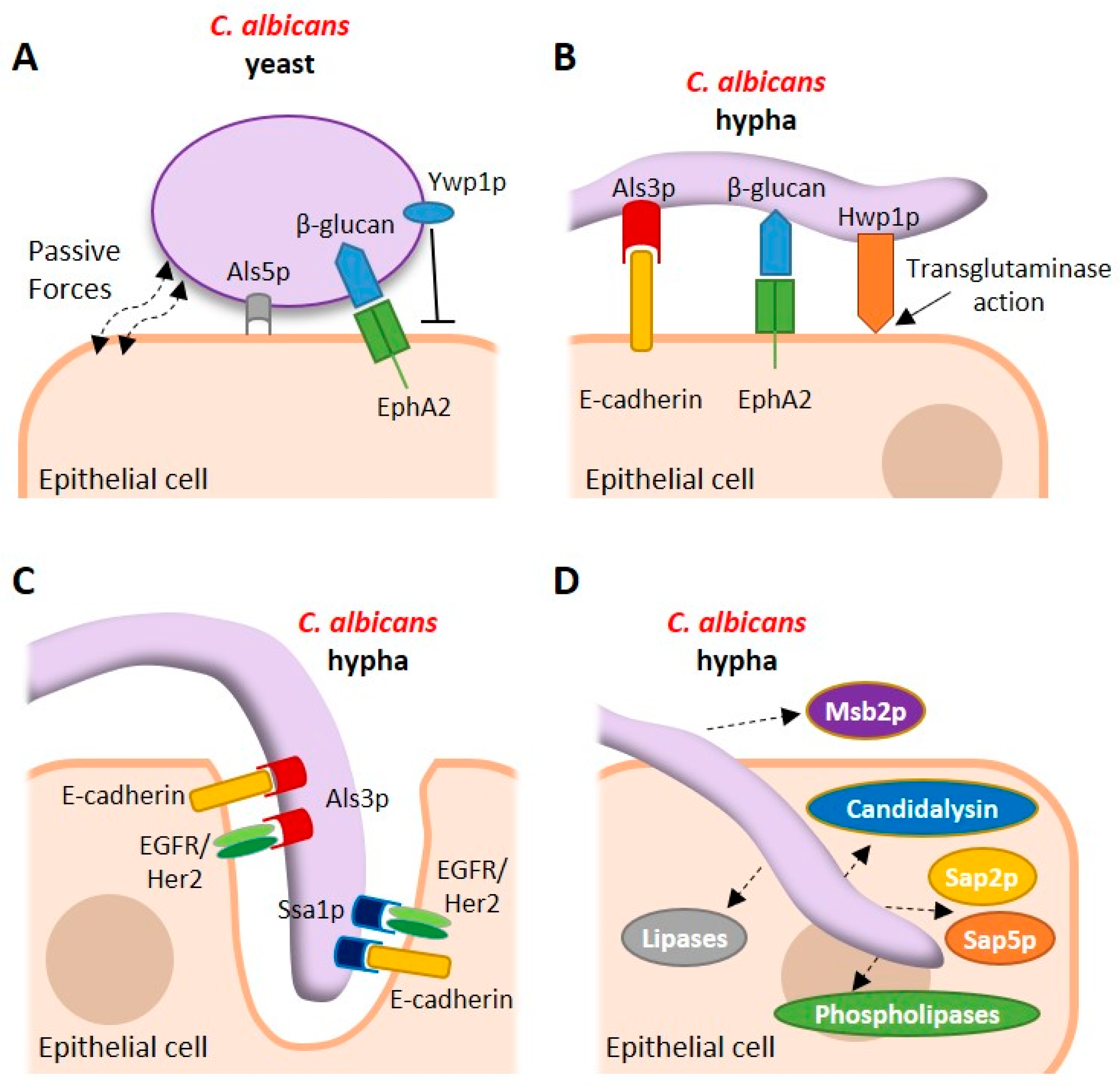
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans Interactions with Mucosal Surfaces during Health and Disease
2POC: The crystal structure of isomerase domain of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase from Candida albicans
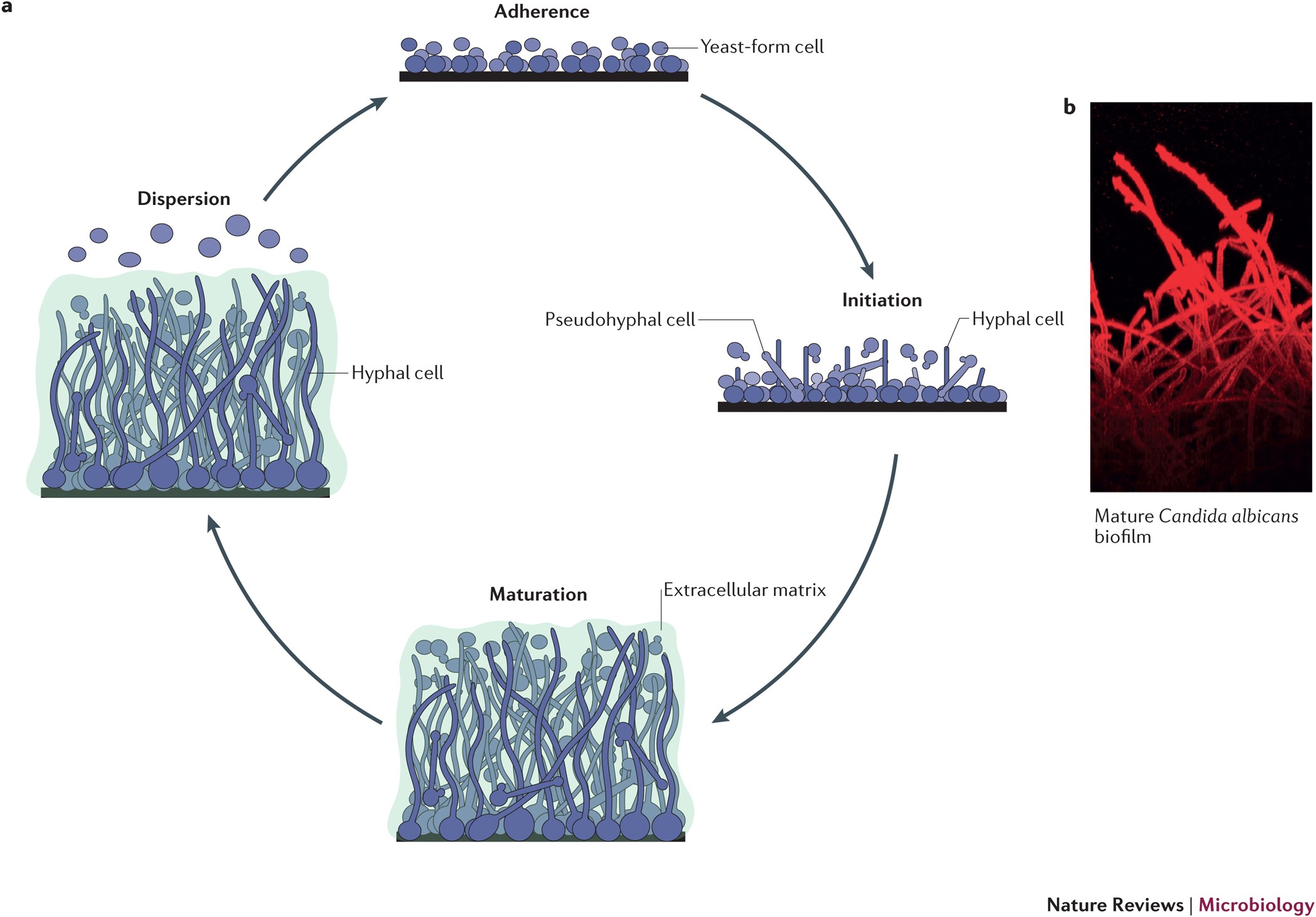
Development and regulation of single- and multi-species Candida albicans biofilms | Nature Reviews Microbiology
Xâ•'ray structures of Sap1 and Sap5: Structural comparison of the secreted aspartic proteinases from <i>Candida albic
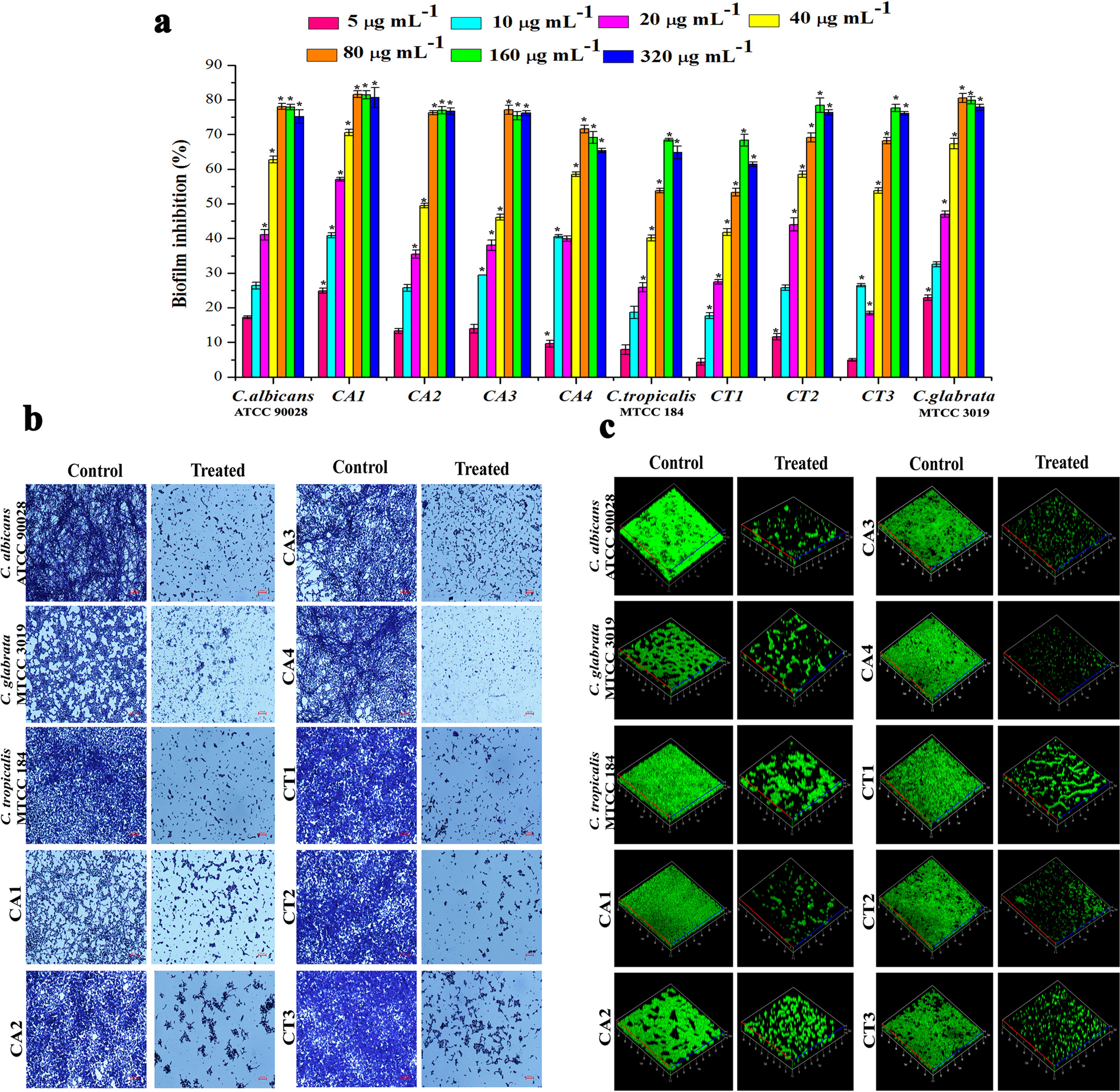
Global proteomic analysis deciphers the mechanism of action of plant derived oleic acid against Candida albicans virulence and biofilm formation | Scientific Reports

Visualizing Biomaterial Degradation by Candida albicans Using Embedded Luminescent Molecules To Report on Substrate Digestion and Cellular Uptake of Hydrolysate | ACS Applied Bio Materials

Global Secretome Characterization of the Pathogenic Yeast Candida glabrata | Journal of Proteome Research
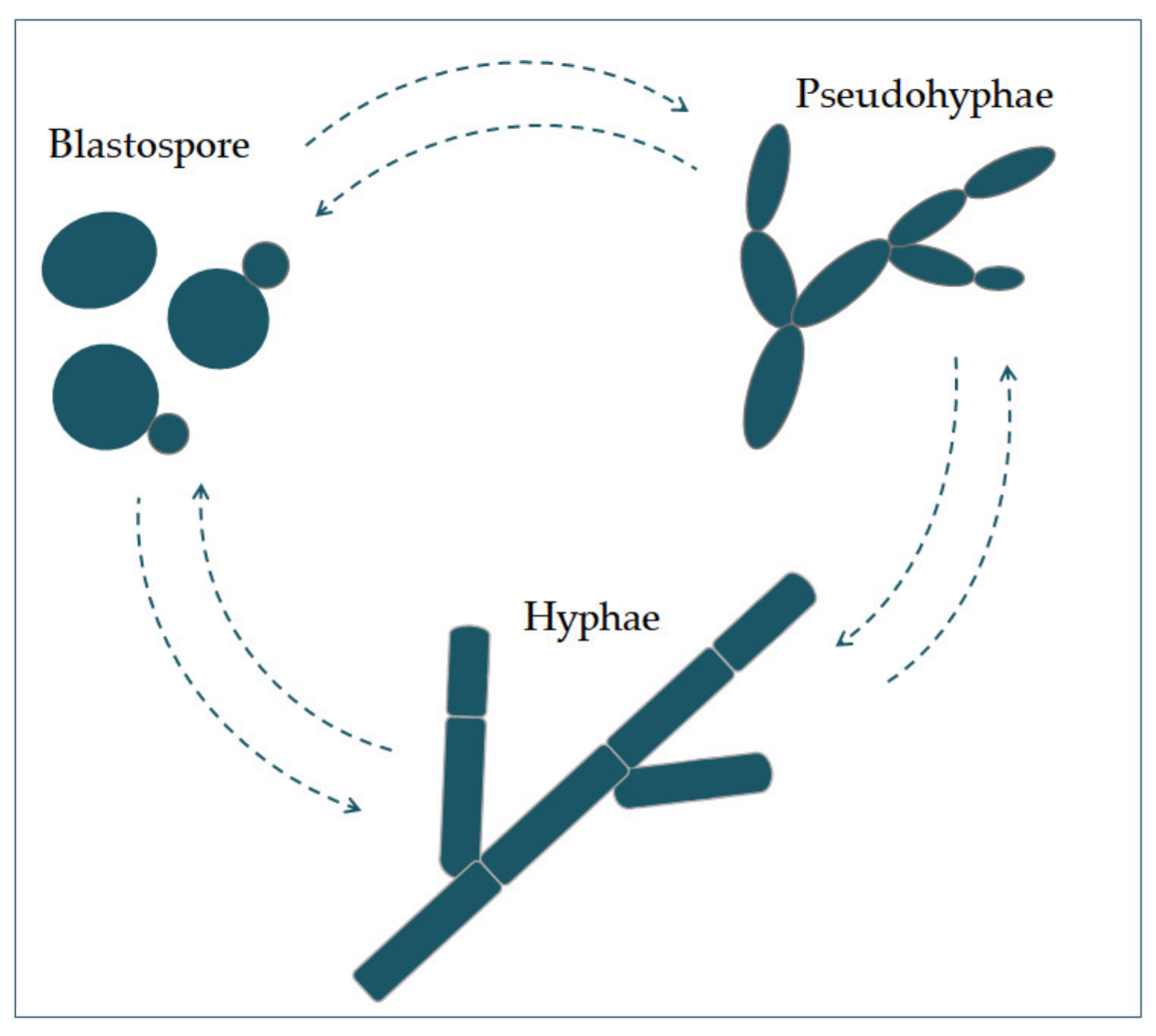
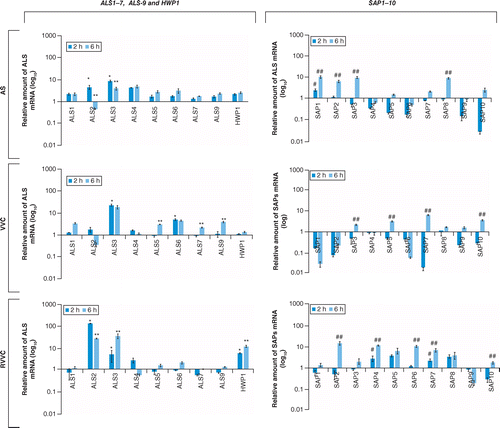
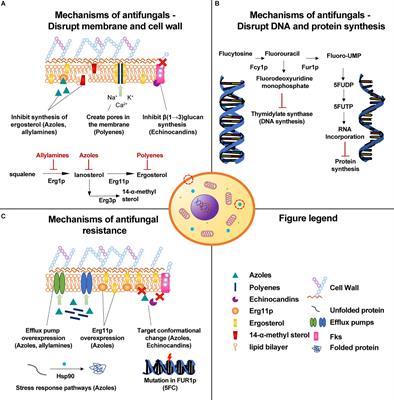
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans—The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection
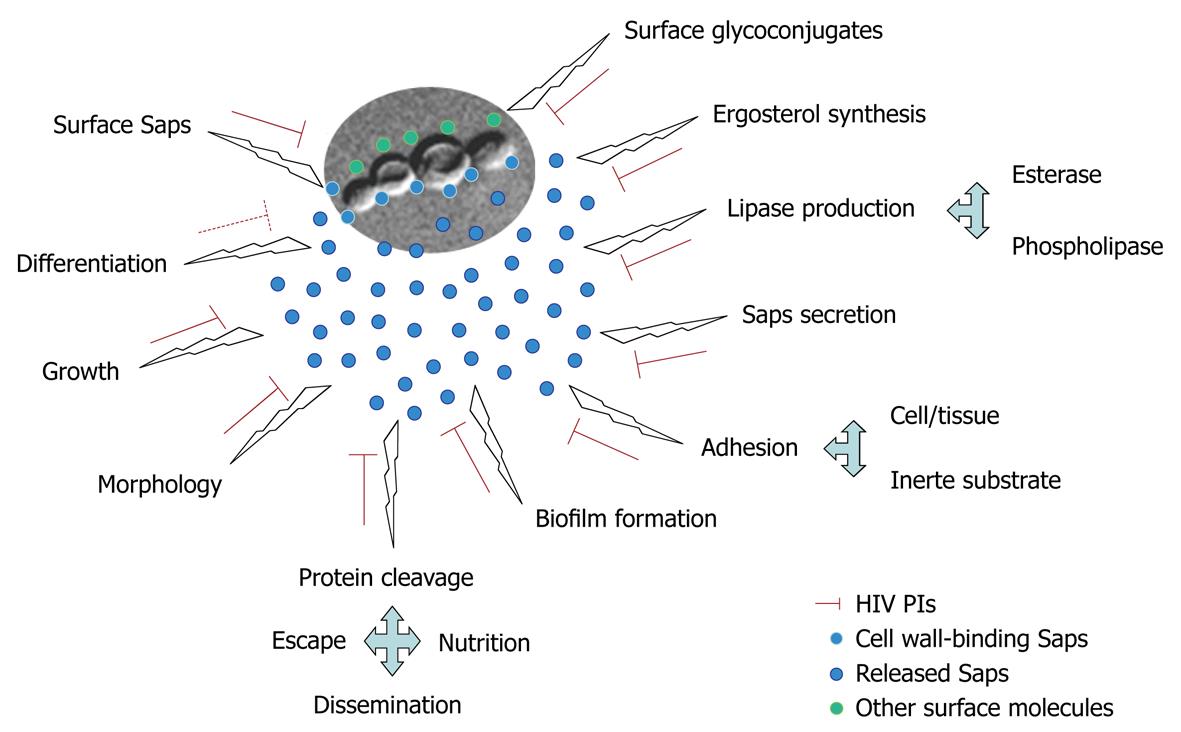
HIV aspartyl protease inhibitors as promising compounds against Candida albicans André Luis Souza dos Santos
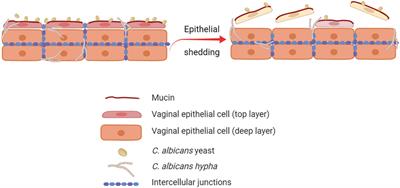
Frontiers | It Takes Two to Tango: How a Dysregulation of the Innate Immunity, Coupled With Candida Virulence, Triggers VVC Onset
The Candida albicans Ku70 Modulates Telomere Length and Structure by Regulating Both Telomerase and Recombination | PLOS ONE

Molecular docking: Bioactive compounds of Mimosa pudica as an inhibitor of Candida albicans Sap 3 | bioRxiv

JoF | Free Full-Text | Repositioning Lopinavir, an HIV Protease Inhibitor, as a Promising Antifungal Drug: Lessons Learned from Candida albicans—In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches